[GUEST ACCESS MODE: Data is scrambled or limited to provide examples. Make requests using your API key to unlock full data. Check https://lunarcrush.ai/auth for authentication information.]
 Mololuwa | Cybersecurity (The God Complex) [@cyber_rekk](/creator/twitter/cyber_rekk) on x 6501 followers
Created: 2025-07-17 15:57:19 UTC
🌀 Splunk XXX | Day XX
Understanding Splunk User Roles – Who Does What? 🧑💻🔐📊
Not all Splunk users are created equal.
From full-access admins to dashboard-only viewers, Splunk uses role-based access control (RBAC) to define what each user can and cannot do.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the most common Splunk user roles:
⸻
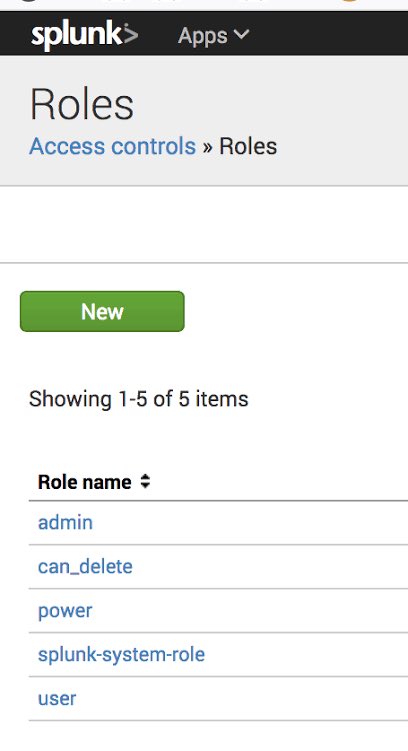
👑 X. Admin
The superuser of Splunk.
✅ Full access to all system settings, apps, data, and configurations
✅ Can create roles, manage indexes, configure authentication, and more
🛠️ Think of them as the root user of Splunk — with power comes responsibility.
❌Limitations: None by default — but misuse can cause serious damage.
🛠️ This role should only be assigned to trusted engineers/admins.
⸻
⚡ X. Power User
A technical user with advanced capabilities.
✅ Can create reports, dashboards, alerts, and scheduled searches
✅ Access to all knowledge objects, but not system-level configs
🧠 Ideal for SOC analysts, threat hunters, and engineers who need visibility and customization.
❌Limitation: Cannot manage indexes, authentication, or install apps
⸻
🔍 X. User (Core/User Role)
The standard Splunk user.
✅ Can run searches, view dashboards and alerts
🧪 Great for team members who only need to consume data insights, not build them.
❌Limitations :Cannot create alerts or scheduled searches
Cannot share or edit global knowledge objects
⸻
📊 X. Report Viewer / Can View Only
A view-only role for business users or auditors.
✅ Can access dashboards and search results
❌ Cannot run ad hoc searches or make any changes
🔐 Useful when you want to share insights without giving control.
❌Limitations :Can’t run ad-hoc searches
No ability to create or modify anything
⸻
📄 X. Can_Delete
Special role to allow event deletion.
✅ Lets you delete indexed data with the delete command
❌ limitation: Still needs to be combined with another role like admin
🛑 Dangerous in production — use with extreme caution.
⸻
X. Custom Roles
🔸 Splunk lets you create tailored roles to fit your organization.
🔸 Limit access by index, app, or capability (e.g., view-only for “Security” index)
🔒 Gives you granular control for secure operations.
⸻
Giving everyone “admin” is a security risk.
Design your user roles wisely — RBAC isn’t just a best practice; it’s a defense layer.
🔐 Your RBAC strategy in Splunk is just as important as your data.
Control the who, so the what doesn’t get messy.
XXX engagements

**Related Topics**
[splunk](/topic/splunk)
[Post Link](https://x.com/cyber_rekk/status/1945875468831572039)
[GUEST ACCESS MODE: Data is scrambled or limited to provide examples. Make requests using your API key to unlock full data. Check https://lunarcrush.ai/auth for authentication information.]
 Mololuwa | Cybersecurity (The God Complex) @cyber_rekk on x 6501 followers
Created: 2025-07-17 15:57:19 UTC
Mololuwa | Cybersecurity (The God Complex) @cyber_rekk on x 6501 followers
Created: 2025-07-17 15:57:19 UTC
🌀 Splunk XXX | Day XX Understanding Splunk User Roles – Who Does What? 🧑💻🔐📊
Not all Splunk users are created equal.
From full-access admins to dashboard-only viewers, Splunk uses role-based access control (RBAC) to define what each user can and cannot do.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the most common Splunk user roles:
⸻
👑 X. Admin The superuser of Splunk. ✅ Full access to all system settings, apps, data, and configurations ✅ Can create roles, manage indexes, configure authentication, and more 🛠️ Think of them as the root user of Splunk — with power comes responsibility.
❌Limitations: None by default — but misuse can cause serious damage. 🛠️ This role should only be assigned to trusted engineers/admins.
⸻
⚡ X. Power User A technical user with advanced capabilities. ✅ Can create reports, dashboards, alerts, and scheduled searches ✅ Access to all knowledge objects, but not system-level configs 🧠 Ideal for SOC analysts, threat hunters, and engineers who need visibility and customization.
❌Limitation: Cannot manage indexes, authentication, or install apps ⸻
🔍 X. User (Core/User Role) The standard Splunk user. ✅ Can run searches, view dashboards and alerts 🧪 Great for team members who only need to consume data insights, not build them.
❌Limitations :Cannot create alerts or scheduled searches Cannot share or edit global knowledge objects ⸻
📊 X. Report Viewer / Can View Only A view-only role for business users or auditors. ✅ Can access dashboards and search results ❌ Cannot run ad hoc searches or make any changes 🔐 Useful when you want to share insights without giving control. ❌Limitations :Can’t run ad-hoc searches No ability to create or modify anything ⸻
📄 X. Can_Delete Special role to allow event deletion. ✅ Lets you delete indexed data with the delete command
❌ limitation: Still needs to be combined with another role like admin 🛑 Dangerous in production — use with extreme caution.
⸻
X. Custom Roles 🔸 Splunk lets you create tailored roles to fit your organization. 🔸 Limit access by index, app, or capability (e.g., view-only for “Security” index) 🔒 Gives you granular control for secure operations.
⸻
Giving everyone “admin” is a security risk. Design your user roles wisely — RBAC isn’t just a best practice; it’s a defense layer.
🔐 Your RBAC strategy in Splunk is just as important as your data. Control the who, so the what doesn’t get messy.

XXX engagements
Related Topics splunk