[GUEST ACCESS MODE: Data is scrambled or limited to provide examples. Make requests using your API key to unlock full data. Check https://lunarcrush.ai/auth for authentication information.]  د.محمد الحربي [@Mhmd_OD](/creator/twitter/Mhmd_OD) on x 19.7K followers Created: 2025-07-12 14:38:27 UTC 🛑 Retinoscopy clinical hints 👁️👁️ 🔹 A retinoscope objectively determine the spherocylindrical refractive error and irregular astigmatism, and also evaluate opacities and irregularities of the cornea and lens. 🔹 Most retinoscope today use a streak projection system. This streak of light is reflected from a mirror. 🔹 Normally, the examiner will use their right eye to perform retinoscopy on the patient's right eye and their left eye for the patient's left eye. 🔹 The examiner should align themselves just off-center to minimize lens reflections and to allow the patient to visualize the distance target to relax their accommodation. 🔹 The patient should be instructed( from time to time ) to look at a distance target such as a large Snellen letter (20/200-20/400). 🔹 When doing retinoscopy, the examiner is attempting to put the far point of the patient’s eye at the plane of the examiner’s pupil. 🔹 When the reflex shows “against” motion, the far point plane lies between the patient’s eye and the examiner’s eye, indicating myopia. 🔹 When the reflex shows “with” motion, the far point lies outside the interval between (the patient’s eye and the observer’s eye), indicating hyperopia, emmetropia or mild myopia. 🔹 The goal of neutralization is to have the light reflex of the patient’s far point at the peephole. 🔹 The light at the patient’s pupil fills the entire space at once when neutrality is reached. 🔹 “With” motion requires more plus to be added to the prescription to move the far point to neutralization. 🔹 “Against” motion means that the far point is in front of the peephole. Therefore, more minus must be added to move the far point to neutralization. 🔵 Retinoscopy step by step ROOM LIGHTS OFF 💡💡💡 🔹 Ask patient to look at a non-accommodative target distance (green duochrome). 🔹 Compensate your working distance ( if you work at 2/3m, add +1.50 D DS). 🔹 Fog fellow eye with a high plus powered lens to prevent accommodation. 🔹 Aim to be as close to the patient’s visual axis without obscuring their fixation target. 🔹 If your head gets in the way, they are likely to look at it and start accommodating. 🔹 Ask the patient to tell you if this happens. 🔹 Check retinoscopy reflex: 🔹 Identify axis of astigmatism from movement of retinoscopy light as sweep across eye. 🔹 Neutralize reflex in one meridian with DS lenses. 🔹 If reflex is (with) then add PLUS, if (against) then add MINUS. 🔹 When point of reversal is reached in one meridian add cylindrical lenses to neutralize in the other meridian. 🔹 Use Plus or minus cylinders and Be consistent either work with plus or with minus cylindrical lenses. 🔹 If using PLUS cylindrical lenses, correct the most MINUS meridian . 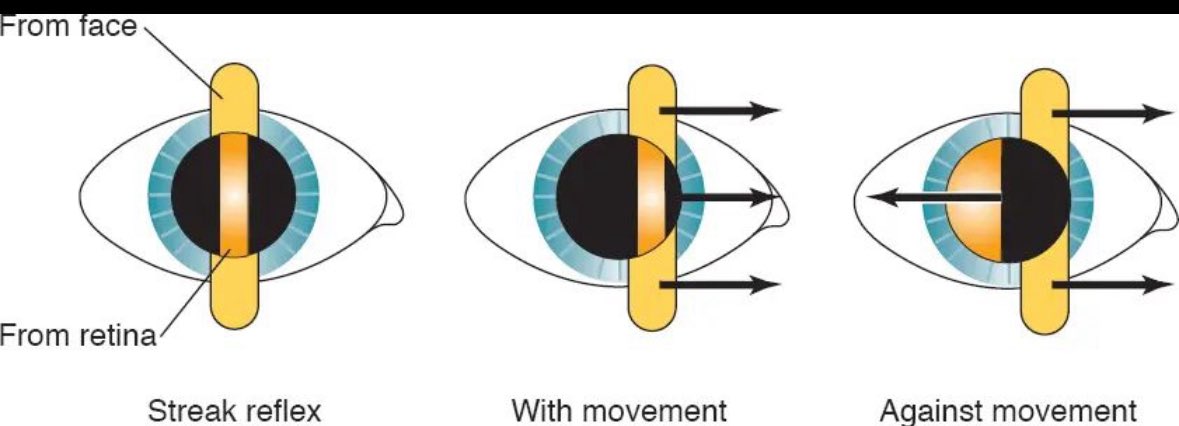 XXXXX engagements  [Post Link](https://x.com/Mhmd_OD/status/1944043682216173790)
[GUEST ACCESS MODE: Data is scrambled or limited to provide examples. Make requests using your API key to unlock full data. Check https://lunarcrush.ai/auth for authentication information.]
 د.محمد الحربي @Mhmd_OD on x 19.7K followers
Created: 2025-07-12 14:38:27 UTC
د.محمد الحربي @Mhmd_OD on x 19.7K followers
Created: 2025-07-12 14:38:27 UTC
🛑 Retinoscopy clinical hints 👁️👁️
🔹 A retinoscope objectively determine the spherocylindrical refractive error and irregular astigmatism, and also evaluate opacities and irregularities of the cornea and lens.
🔹 Most retinoscope today use a streak projection system. This streak of light is reflected from a mirror.
🔹 Normally, the examiner will use their right eye to perform retinoscopy on the patient's right eye and their left eye for the patient's left eye.
🔹 The examiner should align themselves just off-center to minimize lens reflections and to allow the patient to visualize the distance target to relax their accommodation.
🔹 The patient should be instructed( from time to time ) to look at a distance target such as a large Snellen letter (20/200-20/400).
🔹 When doing retinoscopy, the examiner is attempting to put the far point of the patient’s eye at the plane of the examiner’s pupil.
🔹 When the reflex shows “against” motion, the far point plane lies between the patient’s eye and the examiner’s eye, indicating myopia.
🔹 When the reflex shows “with” motion, the far point lies outside the interval between (the patient’s eye and the observer’s eye), indicating hyperopia, emmetropia or mild myopia.
🔹 The goal of neutralization is to have the light reflex of the patient’s far point at the peephole.
🔹 The light at the patient’s pupil fills the entire space at once when neutrality is reached.
🔹 “With” motion requires more plus to be added to the prescription to move the far point to neutralization.
🔹 “Against” motion means that the far point is in front of the peephole. Therefore, more minus must be added to move the far point to neutralization.
🔵 Retinoscopy step by step
ROOM LIGHTS OFF 💡💡💡
🔹 Ask patient to look at a non-accommodative target distance (green duochrome).
🔹 Compensate your working distance ( if you work at 2/3m, add +1.50 D DS).
🔹 Fog fellow eye with a high plus powered lens to prevent accommodation.
🔹 Aim to be as close to the patient’s visual axis without obscuring their fixation target.
🔹 If your head gets in the way, they are likely to look at it and start accommodating.
🔹 Ask the patient to tell you if this happens.
🔹 Check retinoscopy reflex:
🔹 Identify axis of astigmatism from movement of retinoscopy light as sweep across eye.
🔹 Neutralize reflex in one meridian with DS lenses.
🔹 If reflex is (with) then add PLUS, if (against) then add MINUS.
🔹 When point of reversal is reached in one meridian add cylindrical lenses to neutralize in the other meridian.
🔹 Use Plus or minus cylinders and Be consistent either work with plus or with minus cylindrical lenses.
🔹 If using PLUS cylindrical lenses, correct the most MINUS meridian .

XXXXX engagements