[GUEST ACCESS MODE: Data is scrambled or limited to provide examples. Make requests using your API key to unlock full data. Check https://lunarcrush.ai/auth for authentication information.]
 Peter Clack @PeterDClack on x 38.6K followers
Created: 2025-07-18 23:59:05 UTC
Peter Clack @PeterDClack on x 38.6K followers
Created: 2025-07-18 23:59:05 UTC
Airborne CO₂ has collapsed over geological time from XXXXX ppm in the Cambrian (541mya) to XXX ppm only 20K years ago. Its decline is a deadlier threat to survival than hysteria over a warming spell. Today, XX% of all CO₂ is in the oceans, which outgas it when seas are warm. CO₂ is far rarer & more precious than you might think. It's the basis for photosynthesis, supporting every food chain on earth & the air we breathe.
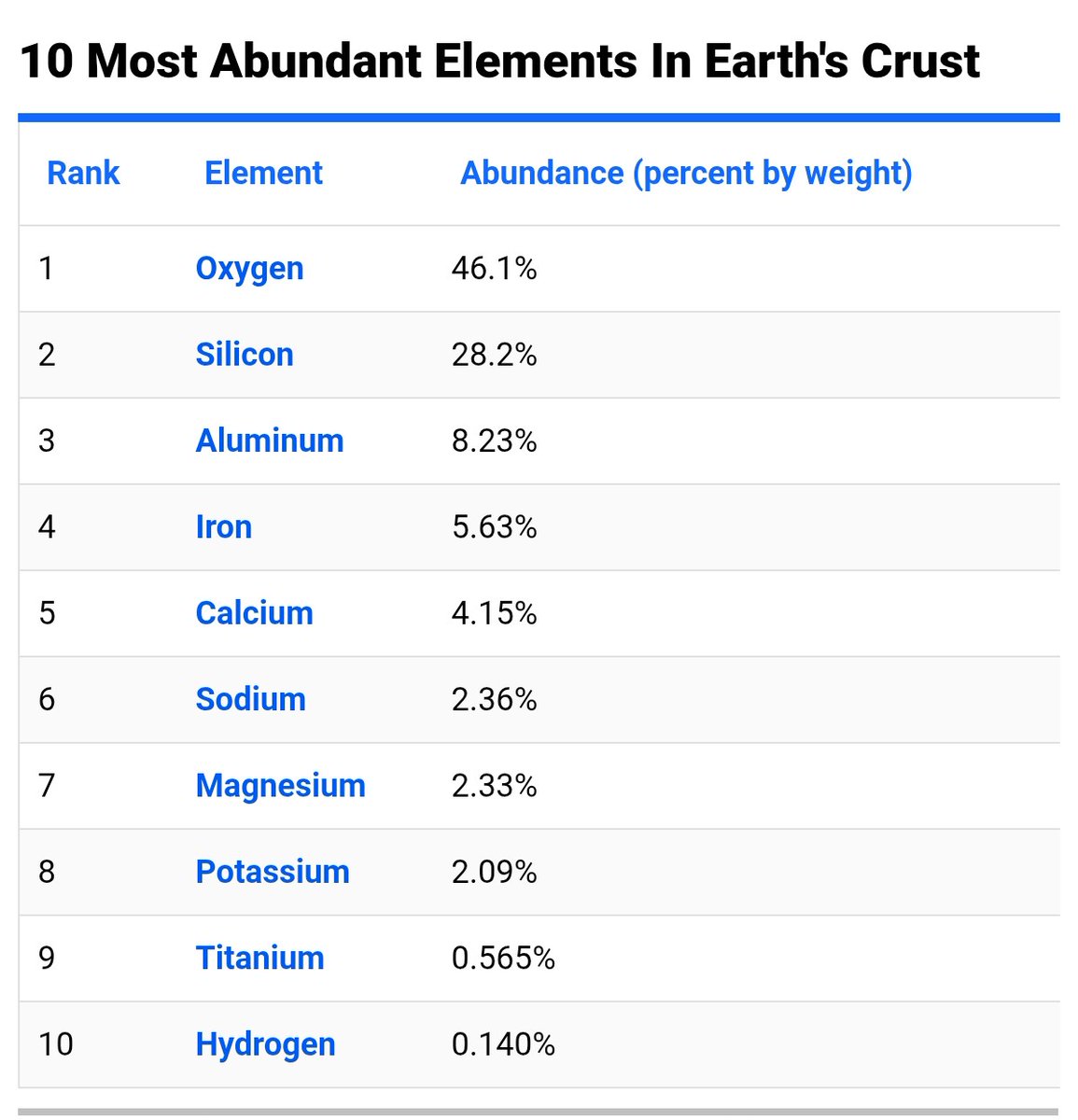
The facts Carbon is not even in the top XX elements in the earth's crust. CO₂ is definitely not in control of world climate or the weather cycles. This is the distortion the UN makes in its swindle about this life-giving compound of carbon & oxygen. The carbon cycle describes the continuous movement of carbon atoms between the atmosphere, biosphere, geosphere & hydrosphere. Carbon is constantly exchanged between these reservoirs through various processes like photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition & combustion. Carbon atoms circulate through the atmosphere, oceans, land (including living organisms & soil) & Earth's crust (rocks & fossil fuels). Photosynthesis Plants & algae absorb CO₂ from the air & sea to produce sugars for energy, storing carbon in their tissues & producing & maintaining all oxygen. Respiration Living organisms, including plants and animals, release CO₂ back into the atmosphere through respiration. Decomposition When organisms die, decomposers break down their remains, releasing carbon back into the atmosphere or soil. Ocean exchange Oceans store XX% of all CO₂, acting as both a source & a sink for atmospheric CO₂. Recycling Over very long timescales, carbon is stored in rocks, sediments, living & decomposing matter. It is recycled back into the biosphere through exhalation, volcanic eruptions & rock weathering. Carbon is the building block of life, forming the basis of proteins, carbohydrates & other essential molecules. The carbon cycle influences the availability of nutrients and the health of ecosystems. It is the basis for every food chain on earth.
XXXXXX engagements
Related Topics spell